Глюкокортикостероиды (ГКС) представляют собой группу веществ с максимально выраженными противовоспалительными свойствами, характерными как для системного применения препаратов данной группы, так и для топического использования. Последний путь характеризуется минимальной выраженностью наиболее значимых для ГКС побочных эффектов, типичных для системного применения. Использование топических ГКС широко представлено в дерматологии, где данная группа препаратов является одной из наиболее назначаемых среди амбулаторных пациентов [1]. В гинекологической практике ГКС используются значительно реже, в том числе вследствие значительного уровня настороженности врачей в отношении риска развития нежелательных реакций. Перечень состояний, потенциально требующих назначения ГКС в гинекологии, несоизмеримо узок в сравнении с дерматологией и включает преимущественно поражения слизистой в зоне вульвы неинфекционного (склероатрофический лихен вульвы) и инфекционного (вульвовагинит) генеза. Cклероатрофический лихен вульвы встречается у ограниченного числа пациенток, составляя до 1,7% по данным эпидемиологического исследования (3 года наблюдений, n=1675) [2]. Вульвовагинит (ВВ) является одним из наиболее распространенных гинекологических заболеваний у женщин репродуктивного возраста [3]. Согласно современным данным, около 70% женщин встречались в течение жизни как минимум с одним эпизодом ВВ. В структуре ВВ первое место занимает бактериальный вагиноз (40–50% случаев ВВ с установленной этиологией), высока частота вульвовагинального кандидоза (ВВК) (до 25%), третье место занимает трихомоноз (15–20%) [4]. Анализ педиатрической практики обнаруживает частоту ВВ среди прочих состояний на уровне 62% [5]. Этиотропная терапия, ориентированная на элиминацию причины воспаления, является основой ведения пациенток, но в большинстве случаев не является достаточной для быстрого устранения симптомов. Длительный изнуряющий зуд, жжение, обильные выделения являются причинами выраженного снижения качества жизни пациенток. Международное исследование (5 европейских стран), включавшее опрос респонденток с рецидивирующим ВВК (в финальный анализ вошли данные 620 женщин, средний возраст 31,8±10,5 года), обнаружило, что доля женщин, испытывающих проблемы в связи с болью/дискомфортом, составила 65% против 35% в общей популяции, доля женщин с депрессией/тревожными расстройствами – 53% против 20% (опросник EQ-5D). Полученные результаты позволили авторам предположить, что влияние хронического ВВК на показатели здоровья сопоставимо с влиянием хронической обструктивной болезни легких и бронхиальной астмы [6]. Наиболее эффективной группой препаратов, способных с первых дней применения устранить основные симптомы ВВ, являются ГКС. Цель настоящего обзора – оценка эффективности и безопасности применения топических ГКС в гинекологической практике.
Фармакодинамические характеристики топических ГКС
Мишенью для реализации эффектов ГКС являются ядерные рецепторы. Структура рецептора включает 4 основных домена: N-концевой домен трансактивации (NTD), центральный ДНК-связывающий домен (DBD), C-концевой лиганд-связывающий домен (LBD), шарнирный домен, связывающий DBD и LBD. Выделяют два сигнальных пути: классический (геномный, включающий диссоциацию рецептора и комплекса шаперонов в цитоплазме с последующим транспортом рецептора в ядро клетки, его связыванием с глюкокортикоидчувствительными элементами и влиянием на транскрипцию генов) [7–9] и неклассический (внегеномный, включает неспецифическое взаимодействие с ядерными мембранами и специфическое взаимодействие с цитозольными либо мембранными рецепторами, связанное с изменением активности протеинкиназ) [10, 11]. Рецепторы ГКС встречаются практически во всех органах и тканях. В коже максимальная концентрация отмечается в кератиноцитах и фибробластах, что соответствует таким структурам, как эпидермис и дерма [12, 13]. ГКС также могут взаимодействовать с минералокортикоидными рецепторами, которые обнаруживаются в протоках потовых желез, сальных железах, волосяных фолликулах и эпидермисе [14]. Результатом взаимодействия ГКС с ядерными рецепторами являются отсроченные и длительно персистирующие эффекты, с мембранными и цитозольными рецепторами – преимущественно остро развивающиеся, «быстрые» эффекты. ГКС обладают обширным спектром фармакодинамических эффектов, включающих в качестве мишеней практически все органы и ткани, а также метаболические процессы в организме. С точки зрения практического использования топических ГКС наиболее значимыми являются три основных эффекта: противовоспалительный, иммуносупрессивный и цитостатический. Противовоспалительный эффект ГКС базируется на способности подавлять синтез медиаторов воспаления вследствие угнетения фосфолипазы А2, в том числе за счет синтеза липокортина и аннексина А1 [15], подавления транскрипции ряда провоспалительных факторов, что модулирует экспрессию генов, отвечающих как за провоспалительные, так и противовоспалительные эффекты. Дополнительный вклад вносит ГКС-опосредуемая вазоконстрикция в верхних слоях дермы, препятствующая доставке клеток крови и медиаторов воспаления [16]. Иммуносупрессивное и антимитотическое действия ГКС опосредуются их плейотропными эффектами на большое число генов: по данным Galon J. et al., до 20% всего генома человека может регулироваться ГКС [17]. Антимитотический эффект топических ГКС реализуется за счет угнетения эпидермального митоза на фоне увеличения концентраций липокортина, подавления синтеза коллагена (проявления катаболического действия ГКС в целом). Доказан эффект подавления индукции экспрессии гена кератина под действием ГКС [18]. Иммуносупрессия при топическом применении ГКС не включает механизмы влияния на Т- и В-лимфоциты, клетки костного мозга и процессы их созревания. В рамках катаболической и иммуносупрессивной активности ГКС отмечается снижение концентрации иммуноглобулинов [19], что может локально проявляться снижением уровня секреторного IgA.
Побочные эффекты при использовании топических ГКС включают две группы: местные (наиболее распространенные) и системные (выраженность зависит от свойств молекулы ГКС и зоны аппликации). Среди местных эффектов в гинекологической практике лидирующим побочным эффектом являются атрофические процессы в зоне вульвы [20, 21]. Общие данные о побочных эффектах топических ГКС со стороны кожи и эпидермиса приведены в таблице 1.
Факторы, определяющие эффективность и безопасность ГКС для местного применения
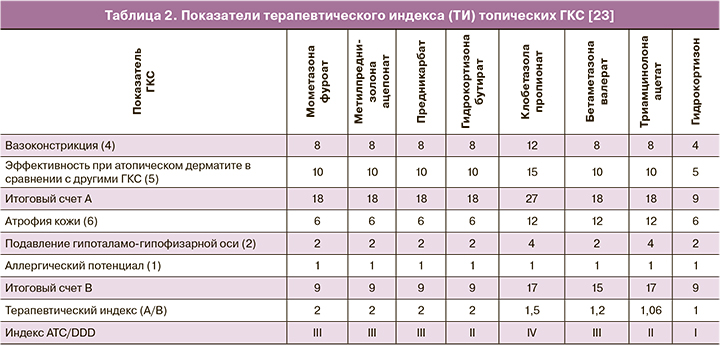
Параметры эффективности и профиль безопасности топических ГКС зависят от химического строения молекул. Химическая модификация, удаление одной или обоих гидрофильных 16- или 17-гидроксильных групп или присоединение длинных углеродных боковых цепей (ацетониды, валераты или пропионаты) увеличивают липофильность ГКС [15]. Идеальная молекула топического ГКС должна формировать терапевтическую концентрацию в клетке-мишени кожи посредством прохождения через роговой слой, но не проникать в системный кровоток во избежание системных побочных эффектов [1]. Липофильность топических ГКС является основным фактором, обеспечивающим проникновение молекул препарата через мембраны клеток и слои кожи. Изменение химической структуры путем галогенирования увеличивает силу действия и эффективность препаратов с параллельным увеличением числа и выраженности их потенциально неблагоприятных эффектов. Изменение путем этерификации способно повышать силу действия на фоне высокого профиля безопасности препарата [23]. Топические ГКС, как липо-, так и гидрофильные, могут формировать резервуар в разнообразных структурах (эпидермис, дерма); определяющими факторами со стороны молекулы ГКС являются степень липофильности и аффинитета к белкам [24]. Интегральным показателем, отражающим совокупность силы действия и эффективности топического ГКС в сочетании с потенциалом препарата вызывать побочные эффекты (локальные и местные), является терапевтический индекс (ТИ), значения которого для различных топических ГКС продемонстрированы в таблице 2.
Следующим значимым фактором, определяющим величину как терапевтического эффекта ГКС, так и выраженность побочных эффектов, является лекарственная форма, а именно такие ее характеристики, как используемая основа и концентрация ГКС. Для таких форм, как мази, кремы, лосьоны, гели и пены, продемонстрированы разные показатели проникновения через роговой слой и, соответственно, биодоступности (максимальные значения для мазей) [16]. Мази способны создавать выраженный и длительный контакт с поверхностью, соответственно, имеют максимальные значения окклюзии и потенциал для формирования резервуара ГКС [25].
Присутствие в лекарственной форме таких усилителей пенетрации через роговой слой, как амиды, эфиры, эфирные спирты (моноэтиловый эфир диэтиленгликоля), жирные кислоты, гликоли, сульфоксиды (диметилсульфоксид), может способствовать формированию резервуара молекул ГКС в кожных структурах [26, 27]. Длительность применения топических ГКС имеет прямую зависимость с частотой и выраженностью побочных эффектов, как местных, так и системных [22].
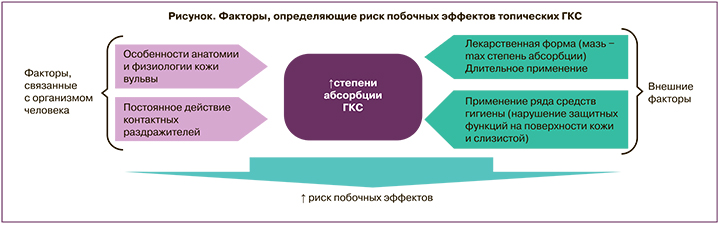
Применение ГКС в гинекологии имеет ряд отличий в сравнении со стандартным использованием топических стероидов. Анатомические и функциональные особенности вульвовагинальной слизистой являются факторами повышенной абсорбции ГКС с поверхности, что приводит к повышению риска развития нежелательных лекарственных реакций [28]. Степень абсорбции стероидов из влагалища определяется толщиной эпителия, величиной рН цервикальной слизи, количеством воды в секрете влагалища. Кожа вульвы характеризуется относительно свободным расположением клеток и отсутствием рогового слоя, что способствует семикратному повышению проницаемости для топических кортикостероидов в сравнении с кожей зоны предплечья [29]. Со стороны лекарственного препарата определяющими факторами абсорбции являются липо/гидрофильность, степень ионизации, молекулярный вес, поверхностный заряд, химическое строение. Побочные эффекты ГКС, возникающие при местном применении в вульвовагинальной области, могут длительное время оставаться незамеченными. Дополнительными триггерами возникновения побочных эффектов являются постоянное воздействие трения, физиологических контактных раздражителей (пот, влагалищные выделения, моча). Использование в вульвовагинальной зоне ГКС с высокой активностью в течение периода, превышающего 1 месяц, может приводить к супрессии надпочечников вследствие высоких показателей системной абсорбции. Соответственно, при местном применении ГКС в вульвовагинальной области необходимо принимать во внимание, что высокая липофильность и высокая топическая активность могут способствовать усилению как местных, так и системных побочных эффектов. Дополнительным фактором является высокое содержание воды в секрете влагалища, что указывает на необходимость наличия гидрофильных свойств у препарата для местного применения: гидрофильность будет определять степень и скорость доставки молекул препарата к слизистой влагалища. Таким образом, комбинация анатомо-физиологических (особенностей строения кожи и слизистой в вульвовагинальной области) и внешних факторов определяет степень риска развития побочных эффектов топических ГКС (рисунок).
Описанные факторы лежат в основе подхода к выбору оптимального местного ГКС для применения в гинекологии. В целом для гинекологического применения местных ГКС препарат должен обладать невысокой активностью и определенными гидрофильными свойствами. В качестве топического ГКС гидрокортизон по силе действия относится к самым слабым препаратам, согласно Американской классификации – VII класс. По данным Британской классификации (British National Formulary (BNF)), гидрокортизона бутират 0,1% крем относится к III классу (умеренные), гидрокортизон 1–2,5% крем, 1–2,5% лосьон, 2,5% мазь, гидрокортизона ацетат 1–2,5% крем, 1–2,5% лосьон, 2,5% мазь – к IV классу [30]. Как правило, ГКС с низкой активностью являются наиболее безопасными средствами для длительного применения на больших площадях поверхности, на лице или на участках с более тонкой кожей, а также слизистой, включая вульвовагинальную область. Соответственно, гидрокортизон при использовании в вульвовагинальной области может обеспечивать высокий профиль безопасности в сравнении с ГКС, обладающими более выраженной активностью. Умеренно активным является также преднизолон. Активность преднизолона превышает таковую для гидрокортизона приблизительно в 5 раз [31]. Большая активность преднизолона позволяет применять его в меньшей дозе в сравнении с гидрокортизоном при местном применении. Тем не менее, принимая во внимание особенности строения слизистой вульвовагинальной области, несколько большая липофильность преднизолона и его относительно высокая активность могут способствовать формированию более высоких значений системной абсорбции, что может вносить вклад в повышение частоты и тяжести побочных эффектов препарата. Гидрокортизон имеет минимальное значение индекса ATC/DDD (данные Gual A. et al., 2015), равное I согласно формуле (отношение эффективности/риска побочных эффектов) [23]. Подробно анализируя каждый из факторов, формирующих счет индекса (степень подавления гипоталамо-гипофизарной оси на фоне системной абсорбции, аллергический потенциал, атрофия кожи – см. табл. 1), можно отметить, что риск побочных эффектов гидрокортизона не превышает минимальных показателей для всех проанализированных топических ГКС, а низкое значение индекса основано в первую очередь на небольших значениях местной активности препарата. В свою очередь, низкая местная активность ГКС при использовании на слизистой влагалища является необходимым условием для местного кортикоида. В случае гидрокортизона ацетата эфирная форма повышает эффективность препарата на фоне снижения показателей системной абсорбции, с одной стороны, с другой – повышает уровень доставки препарата непосредственно к слизистой, так как молекулы могут проходить через влагалищный секрет, состоящий преимущественно из воды. Таким образом, обсуждая перспективы местного использования гидрокортизона в гинекологии, можно отметить, что указанные особенности (низкая местная активность, означающая низкий уровень системной абсорбции для вульвовагинальной области, и низкие показатели рисков возникновения местных нежелательных лекарственных реакций) являются положительными характеристиками, указывающими на возможные терапевтические выгоды применения препарата в данной области. Фармакокинетические параметры топических ГКС в гинекологии, в частности, величина биодоступности, доступны лишь для ограниченного числа ГКС. По данным Burger-Stritt S. et al. (2019), фармакокинетика преднизолона отличалась в случае вагинального и ректального введения суппозиториев. Cmax и AUC0–360 были значительно ниже после вагинального введения по сравнению с ректальным введением: 22 нг/мл (109%) против 161 нг/мл (28%), P<0,001; 4390 нг/мл×мин (116%) против 40 302 нг/мл×мин (26%), P<0,001 (среднее (коэффициент вариации) соответственно) [32].
Данные системной абсорбции при вагинальном использовании гидрокортизона отсутствуют, косвенное сравнение возможно при интерпретации данных при ректальном пути введения препарата. Tromm A. et al. (2001) приводят данные о параметрах абсорбции ректальной формы гидрокортизона ацетата (100 мг, пена): среднее значение биодоступности составило 3,1% для здоровых добровольцев и 4,5% для пациентов с колитом [33]. По данным Möllmann H. еt al. (1991), ректальное введение гидрокортизона ацетата (100 мг) характеризовалось средним значением биодоступности, равным 2% [34]. В целом величина системной абсорбции при ректальном пути введения превосходит таковую для вагинального пути, соответственно, можно предположить, что вагинальная абсорбция гидрокортизона будет иметь абсолютно незначительные значения.
Клиническая эффективность
Эффективность и безопасность применения топических ГКС в гинекологии подтверждены клиническими рекомендациями, а также результатами опубликованных работ. Европейские клинические рекомендации по ведению пациенток с патологическими состояниями в зоне вульвы (2016) включают назначение сильнодействующих топических ГКС при тяжелых формах лихена и более слабых препаратов, таких как 1% гидрокортизон в виде мази, крема и пены при различных формах дерматитов в зоне вульвы и при вульводинии [35]. Согласно данным Anderson M. et al. (2002), использование вагинальных свечей, содержащих гидрокортизон, приводило к достоверному улучшению симптоматики у пациенток с вульвовагинальными проявлениями красного плоского лишая, средняя длительность терапии составила 28,1 месяца (n=35), субъективное улучшение было отмечено в 81% случаев, объективное улучшение – в 76,8% [36]. Продемонстрированный в работе длительный период применения гидрокортизона не сопровождался негативной симптоматикой и не приводил к отмене препарата из-за возникновения побочных эффектов, что свидетельствует о высоком профиле безопасности длительного интравагинального использования. Обзор подходов к ведению пациенток с вагинитами, выполненный Fischer G. (2001), включает в качестве препаратов выбора на этапе старта сильнодействующие ГКС (метилпреднизолона ацепонат, бетаметазона валерат) с дальнейшим обязательным переключением на 1% гидрокортизон для длительного применения (1 месяц) [37]. В педиатрической практике в местной терапии неинфекционных вульвитов, дерматитов зоны вульвы, псориатических поражений, склерозирующего лихена рекомендовано применять топические ГКС умеренного либо слабого действия, такие как клобетазола пропионат 0,05%, гидрокортизон 1% [5]. Опубликованные данные преимущественно регламентируют использование топических ГКС при неинфекционных поражениях вульвы [38], тем не менее, данная группа препаратов является распространенным компонентом ведения пациенток с грибковой и бактериальной этиологией вульвовагинитов. Комбинация ГКС, в частности, гидрокортизона, с антибактериальными препаратами и антимикотиками в одной лекарственной форме является эффективным инструментом устранения тяжелой симптоматики [39]. Для устранения симптоматики вульвитов у беременных, включая выраженный зуд, предлагается использовать топические ГКС слабого действия, включая гидрокортизон [40].
Безопасность применения топических ГКС у беременных (преимущественно в дерматологии) была продемонстрирована в обновленной версии Кокрановского обзора, включившего 14 исследований (n=1 601 515) [41]. Результаты продемонстрировали отсутствие причинно-следственных связей между воздействием топических ГКС на мать и исходами беременности (способ родоразрешения, врожденные аномалии, преждевременные роды, смерть плода, низкий балл по шкале Апгар).
В Российской Федерации зарегистрирован препарат для топического (интравагинального) применения для терапии неспецифических вагинитов, содержащий гидрокортизон в виде ацетата (15 мг), а также метронидазол 500 мг, хлорамфеникол 200 мг и натамицин 150 мг (Таржифорт®). Комплексный состав препарата позволяет обеспечить как этиотропное (антибактериальное, антигрибковое и антипротозойное), так и патогенетическое (противовоспалительное) действия, что позволяет быстро устранить типичную для вагинитов симптоматику (зуд, жжение и боль в области гениталий) [42].
Заключение
Использование топических ГКС в гинекологии является актуальным направлением симптоматической терапии как неинфекционных состояний, так и вульвовагинитов бактериальной либо грибковой этиологии. Особенности строения кожных покровов и слизистых в данной области предполагает более высокий уровень системной абсорбции в сравнении с применением в дерматологии, что может вносить вклад в повышение риска системных побочных эффектов. Топические ГКС минимальной силы, включая гидрокортизон в низких концентрациях, являются препаратами выбора для длительного применения, в том числе у беременных с выраженной симптоматикой вульвитов и вульвовагинитов различной этиологии.



